Background and Motivation
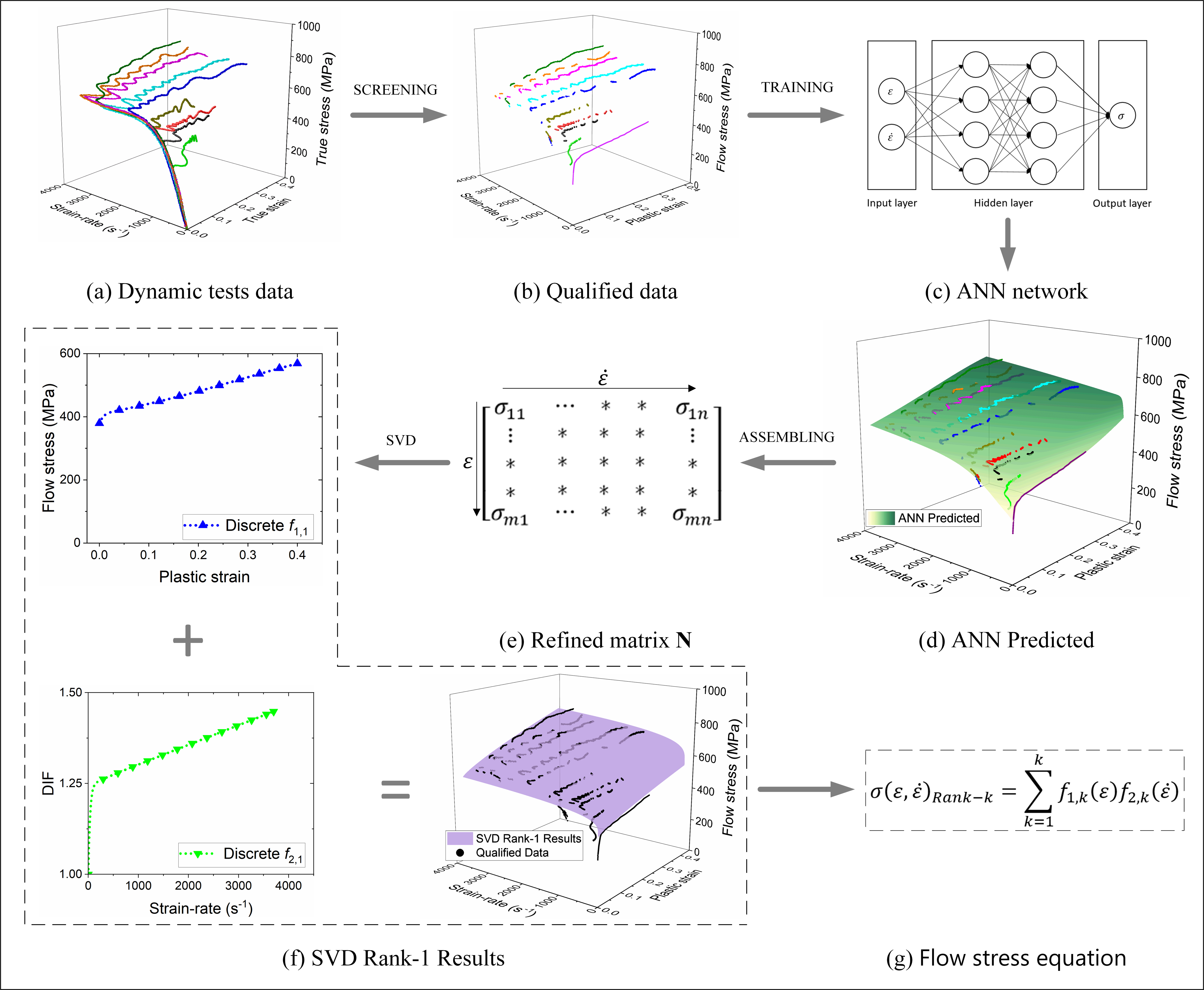
Accurate determination of dynamic flow stress is fundamental for modelling material behaviour under high strain-rate loading. Conventional split Hopkinson pressure bar (SHPB)–based methods typically assume a constant strain-rate and rely on averaged values, which may obscure the intrinsic dependence of flow stress on instantaneous strain-rate.
In practice, SHPB experiments naturally involve varying strain-rates, leading to discrete and sparsely distributed flow stress data in strain–strain-rate space. Existing approaches are not well suited to fully exploit such data and may introduce significant uncertainty in the resulting constitutive equations.
Motivated by these limitations, this work proposes a data-driven framework that integrates qualified SHPB data, artificial neural networks, and singular value decomposition to determine dynamic flow stress equations directly from discrete experimental datasets. The methodology aims to improve accuracy, reliability, and data efficiency in the characterization of strain-rate–dependent material behaviour.
Highlights
•
New methodology to determine dynamic flow stress by SHPB in strain and strain-rate space.
•
SVD are used together with ANN to describe dynamic flow stress.
•
The method has higher accuracy and effectiveness.
Source: Xianglin Huang, Q.M. Li, Determination of dynamic flow stress equation based on discrete experimental data: Part 1 Methodology and the dependence of dynamic flow stress on strain-rate, International Journal of Impact Engineering, Volume 206, 2025, 105403, ISSN 0734-743X, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2025.105403.